
Back Kroniek van het Atlantisch orkaanseizoen 2007 Dutch Cronologia da temporada de furacões no Atlântico de 2007 Portuguese 2007年大西洋飓风季时间轴 Chinese
| Timeline of the 2007 Atlantic hurricane season | |
|---|---|
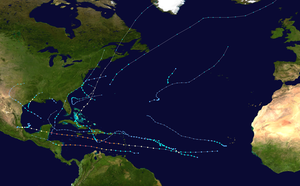 Season summary map | |
| Season boundaries | |
| First system formed | May 9, 2007 |
| Last system dissipated | December 14, 2007 |
| Strongest system | |
| Name | Dean |
| Maximum winds | 175 mph (280 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| Lowest pressure | 905 mbar (hPa; 26.72 inHg) |
| Longest lasting system | |
| Name | Dean |
| Duration | 10 days |
The 2007 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the north Atlantic Ocean. A near average Atlantic hurricane season,[nb 1] September had a record-tying eight storms, although the strength and duration of most of the storms was low.[2] Also, for only the second time in recorded history, an Atlantic hurricane, Felix, and an eastern Pacific hurricane, Henriette, made landfall on the same day.
The season officially began on June 1, 2007, and ended on November 30, 2007, dates that conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones develop in the Atlantic basin.[3] The season's first storm, Subtropical Storm Andrea, developed from an extratropical cyclone that formed on May 6, and the last, Tropical Storm Olga, dissipated on December 11. Altogether, there were 15 named tropical storms during the 2007 season. Six storms attained hurricane strength with two intensifying further into major hurricanes.[nb 2]
This timeline includes information that was not operationally released, meaning that data from post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center, such as a storm that was not operationally warned upon, has been included. This timeline documents tropical cyclone formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, and dissipations during the season.
By convention, meteorologists use one time zone when issuing forecasts and making observations: Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), and also use the 24-hour clock (where 00:00 = midnight UTC).[5] The National Hurricane Center uses both UTC and the time zone where the center of the tropical cyclone is currently located. The time zones utilized (east to west) prior to 2020 were: Atlantic, Eastern, and Central.[6] In this timeline, all information is listed by UTC first with the respective regional time included in parentheses. Additionally, figures for maximum sustained winds and position estimates are rounded to the nearest 5 units (knots, miles, or kilometers), following the convention used in the National Hurricane Center's products. Direct wind observations are rounded to the nearest whole number. Atmospheric pressures are listed to the nearest millibar and nearest hundredth of an inch of mercury.
- ^ Climate Prediction Center Internet Team (August 4, 2011). "Background Information: The North Atlantic Hurricane Season". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Climate Prediction Center. Retrieved January 5, 2013.
- ^ NHC Hurricane Research Division. "Atlantic Hurricane Best Track (1950-present)". NOAA. Archived from the original on 2008-09-16. Retrieved 2008-08-22.
- ^ Dorst, Neal (June 1, 2018). "Hurricane Season Information". Frequently Asked Questions About Hurricanes. Miami, Florida: NOAA Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory. Retrieved June 29, 2020.
- ^ "Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 29, 2020.
- ^ "Understanding the Date/Time Stamps". Miami, Florida: NOAA National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 10, 2020.
- ^ "Update on National Hurricane Center Products and Services for 2020" (PDF). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. April 20, 2020. Retrieved May 17, 2020.
Cite error: There are <ref group=nb> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=nb}} template (see the help page).