| Spherical | Euclidean | Hyperbolic | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 {5,3} 5.5.5 |
 {6,3} 6.6.6 |
 {7,3} 7.7.7 |
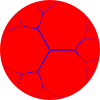 {∞,3} ∞.∞.∞ | ||
| Regular tilings {p,q} of the sphere, Euclidean plane, and hyperbolic plane using regular pentagonal, hexagonal and heptagonal and apeirogonal faces. | |||||
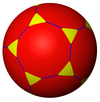 t{5,3} 10.10.3 |
 t{6,3} 12.12.3 |
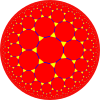 t{7,3} 14.14.3 |
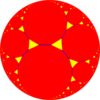 t{∞,3} ∞.∞.3 | ||
| Truncated tilings have 2p.2p.q vertex figures from regular {p,q}. | |||||
 r{5,3} 3.5.3.5 |
 r{6,3} 3.6.3.6 |
 r{7,3} 3.7.3.7 |
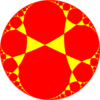 r{∞,3} 3.∞.3.∞ | ||
| Quasiregular tilings are similar to regular tilings but alternate two types of regular polygon around each vertex. | |||||
 rr{5,3} 3.4.5.4 |
 rr{6,3} 3.4.6.4 |
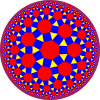 rr{7,3} 3.4.7.4 |
 rr{∞,3} 3.4.∞.4 | ||
| Semiregular tilings have more than one type of regular polygon. | |||||
 tr{5,3} 4.6.10 |
 tr{6,3} 4.6.12 |
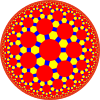 tr{7,3} 4.6.14 |
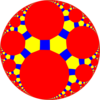 tr{∞,3} 4.6.∞ | ||
| Omnitruncated tilings have three or more even-sided regular polygons. | |||||
| Symmetry | Triangular dihedral symmetry
|
Tetrahedral
|
Octahedral
|
Icosahedral
|
p6m symmetry
|
[3,7] symmetry
|
[3,8] symmetry
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Starting solid Operation |
Symbol {p,q} |
Triangular hosohedron {2,3}  |
Triangular dihedron {3,2}  |
Tetrahedron {3,3}  |
Cube {4,3} |
Octahedron {3,4}  |
Dodecahedron {5,3} 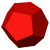 |
Icosahedron {3,5}  |
Hexagonal tiling {6,3}  |
Triangular tiling {3,6}  |
Heptagonal tiling {7,3}  |
Order-7 triangular tiling {3,7}  |
Octagonal tiling {8,3}  |
Order-8 triangular tiling {3,8} 
|
| Truncation (t) | t{p,q} |
triangular prism |
truncated triangular dihedron (Half of the "edges" count as degenerate digon faces. The other half are normal edges.) (Half of the "edges" count as degenerate digon faces. The other half are normal edges.) |
truncated tetrahedron |
truncated cube |
truncated octahedron |
truncated dodecahedron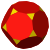 |
truncated icosahedron |
Truncated hexagonal tiling |
Truncated triangular tiling |
Truncated heptagonal tiling |
Truncated order-7 triangular tiling |
Truncated octagonal tiling |
Truncated order-8 triangular tiling
|
| Rectification (r) Ambo (a) |
r{p,q} |
tridihedron (All of the "edges" count as degenerate digon faces.) (All of the "edges" count as degenerate digon faces.) |
tetratetrahedron |
cuboctahedron |
icosidodecahedron |
Trihexagonal tiling |
Triheptagonal tiling |
Trioctagonal tiling
| ||||||
| Bitruncation (2t) Dual kis (dk) |
2t{p,q} |
truncated triangular dihedron (Half of the "edges" count as degenerate digon faces. The other half are normal edges.) (Half of the "edges" count as degenerate digon faces. The other half are normal edges.) |
triangular prism |
truncated tetrahedron |
truncated octahedron |
truncated cube |
truncated icosahedron |
truncated dodecahedron |
truncated triangular tiling |
truncated hexagonal tiling |
Truncated order-7 triangular tiling |
Truncated heptagonal tiling |
Truncated order-8 triangular tiling |
Truncated octagonal tiling
|
| Birectification (2r) Dual (d) |
2r{p,q} |
triangular dihedron {3,2}  |
triangular hosohedron {2,3}  |
tetrahedron |
octahedron |
cube |
icosahedron |
dodecahedron |
triangular tiling |
hexagonal tiling |
Order-7 triangular tiling |
Heptagonal tiling |
Order-8 triangular tiling |
Octagonal tiling
|
| Cantellation (rr) Expansion (e) |
rr{p,q} |
triangular prism (The "edge" between each pair of tetragons counts as a degenerate digon face. The other edges (the ones between a trigon and a tetragon) are normal edges.) (The "edge" between each pair of tetragons counts as a degenerate digon face. The other edges (the ones between a trigon and a tetragon) are normal edges.) |
rhombitetratetrahedron |
rhombicuboctahedron |
rhombicosidodecahedron  |
rhombitrihexagonal tiling |
Rhombitriheptagonal tiling  |
Rhombitrioctagonal tiling 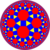
| ||||||
| Snub rectified (sr) Snub (s) |
sr{p,q} |
triangular antiprism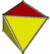 (Three yellow-yellow "edges", no two of which share any vertices, count as degenerate digon faces. The other edges are normal edges.) (Three yellow-yellow "edges", no two of which share any vertices, count as degenerate digon faces. The other edges are normal edges.) |
snub tetratetrahedron |
snub cuboctahedron |
snub icosidodecahedron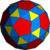 |
snub trihexagonal tiling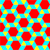 |
Snub triheptagonal tiling |
Snub trioctagonal tiling
| ||||||
| Cantitruncation (tr) Bevel (b) |
tr{p,q} |
hexagonal prism |
truncated tetratetrahedron |
truncated cuboctahedron |
truncated icosidodecahedron |
truncated trihexagonal tiling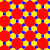 |
Truncated triheptagonal tiling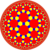 |
Truncated trioctagonal tiling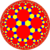
| ||||||
In hyperbolic geometry, a uniform hyperbolic tiling (or regular, quasiregular or semiregular hyperbolic tiling) is an edge-to-edge filling of the hyperbolic plane which has regular polygons as faces and is vertex-transitive (transitive on its vertices, isogonal, i.e. there is an isometry mapping any vertex onto any other). It follows that all vertices are congruent, and the tiling has a high degree of rotational and translational symmetry.
Uniform tilings can be identified by their vertex configuration, a sequence of numbers representing the number of sides of the polygons around each vertex. For example, 7.7.7 represents the heptagonal tiling which has 3 heptagons around each vertex. It is also regular since all the polygons are the same size, so it can also be given the Schläfli symbol {7,3}.
Uniform tilings may be regular (if also face- and edge-transitive), quasi-regular (if edge-transitive but not face-transitive) or semi-regular (if neither edge- nor face-transitive). For right triangles (p q 2), there are two regular tilings, represented by Schläfli symbol {p,q} and {q,p}.
