
Back داء قلبي صمامي Arabic Порок на сърцето Bulgarian Valvulopatia Catalan Chlopenní vada Czech Herzklappenfehler German Valvulopatía Spanish Balbulopatia Basque نارسایی دریچه قلب Persian Sydämen läppäviat Finnish Valvulopathie cardiaque French
| Valvular heart disease | |
|---|---|
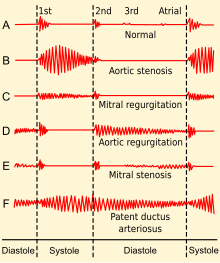 | |
| Phonocardiogram of normal and abnormal heartbeats. | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
| Diagnostic method | Chest radiograph |
Valvular heart disease is any cardiovascular disease process involving one or more of the four valves of the heart (the aortic and mitral valves on the left side of heart and the pulmonic and tricuspid valves on the right side of heart). These conditions occur largely as a consequence of aging,[1] but may also be the result of congenital (inborn) abnormalities or specific disease or physiologic processes including rheumatic heart disease and pregnancy.[2]
Anatomically, the valves are part of the dense connective tissue of the heart known as the cardiac skeleton and are responsible for the regulation of blood flow through the heart and great vessels. Valve failure or dysfunction can result in diminished heart functionality, though the particular consequences are dependent on the type and severity of valvular disease. Treatment of damaged valves may involve medication alone, but often involves surgical valve repair or valve replacement.[citation needed]
- ^ Burden of valvular heart diseases: a population-based study. Nkomo VT, Gardin JM, Skelton TN, Gottdiener JS, Scott CG, Enriquez-Sarano. Lancet. 2006 Sep;368(9540):1005-11.
- ^ Pregnancy and contraception in congenital heart disease: what women are not told. Kovacs AH, Harrison JL, Colman JM, Sermer M, Siu SC, Silversides CK J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52(7):577.
