
Back دائرة مزدوجة Arabic Vesica piscis Byelorussian Vesica Piscis BJN Vesica piscis German Vesica piscis Spanish Vesica piscis French Vesica piscis Galician וסיקה פיסקיס HE Vesica piscis Italian Vesica piscis Latvian/Lettish

The vesica piscis is a type of lens, a mathematical shape formed by the intersection of two disks with the same radius, intersecting in such a way that the center of each disk lies on the perimeter of the other.[1] In Latin, "vesica piscis" literally means "bladder of a fish", reflecting the shape's resemblance to the conjoined dual air bladders (swim bladder) found in most fish.[2] In Italian, the shape's name is mandorla ("almond").[3] A similar shape in three dimensions is the lemon.
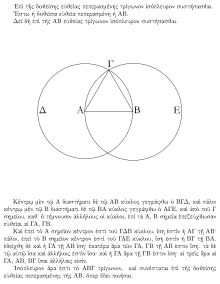
This figure appears in the first proposition of Euclid's Elements, where it forms the first step in constructing an equilateral triangle using a compass and straightedge. The triangle has as its vertices the two disk centers and one of the two sharp corners of the vesica piscis.[4]
- ^ Fletcher, Rachel (2004), "Musings on the Vesica Piscis", Nexus Network Journal, 6 (2): 95–110, doi:10.1007/s00004-004-0021-8.
- ^ Norwood, J. W. (1912), "Fish and water symbols", The Open Court, 1912 (11): 662–672
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
bgswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Heath, Sir Thomas L. (1956), The Thirteen Books of Euclid's Elements (2 ed.), New York: Dover Publications, pp. 241, ISBN 0486600904