
Back حمى نزفية فيروسية Arabic حمى نزفيه فيروسيه ARZ Гемарагічныя ліхаманкі Byelorussian Вирусни хеморагични трески Bulgarian Febre hemorràgica vírica Catalan Virové hemoragické horečky Czech Hämorrhagisches Fieber German Ιογενής αιμορραγικός πυρετός Greek Fiebre hemorrágica viral Spanish Hemorraagiline palavik Estonian
This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. (July 2020) |  |
| Viral hemorrhagic fever | |
|---|---|
| Other names | viral haemorrhagic fever |
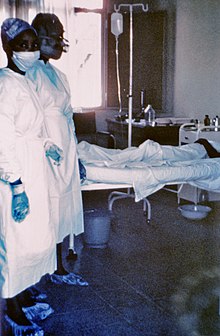 | |
| Two nurses standing near Mayinga N'Seka, a nurse with Ebola virus disease in the 1976 outbreak in Zaire. N'Seka died a few days later due to severe internal hemorrhage. | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a diverse group of diseases. Viral means a health problem caused by infection from a virus. Hemorrhagic means to bleed and fever means an unusually high body temperature. Both humans and non human animals can be infected. In the case of VHFs, bleeding and fever are common symptoms, and why they give the infection its common name.
There are five known families of RNA viruses which causes VHFs: Arenaviridae, Filoviridae, Flaviviridae, Hantaviridae, and Rhabdoviridae. Some VHFs are usually mild, such as nephropathia epidemica (within the family Hantaviridae). But some are usually severe and have a high death rate, such as Ebola virus (within the family Filoviridae). All VHFs can potentially cause severe blood loss, high fever, and death.