
Back Anaxyrus boreas Bulgarian Anaxyrus boreas Catalan Anaxyrus boreas CEB Anaxyrus boreas Spanish Anaxyrus boreas Basque وزغ غربی Persian Crapaud boréal French Anaxyrus boreas Galician קרפדה מערבית HE Anaxyrus boreas Italian
| Western toad | |
|---|---|

| |
| Anaxyrus boreas boreas | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Bufonidae |
| Genus: | Anaxyrus |
| Species: | A. boreas
|
| Binomial name | |
| Anaxyrus boreas | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Bufo boreas Baird & Girard, 1852 | |
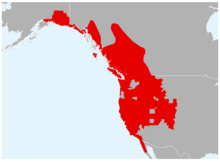
The western toad (Anaxyrus boreas) is a large toad species, between 5.6 and 13 cm (2.2 and 5.1 in) long, native to western North America.[1][3][4] A. boreas is frequently encountered during the wet season on roads, or near water at other times. It can jump a considerable distance for a toad. Breeding occurs between March and July in mountainous areas, and as early as January in lower-elevation regions. The female lays up to 17,000 eggs stuck together in strings that adhere to vegetation and other objects along water edges.[5]
- ^ a b IUCN SSC Amphibian Specialist Group. 2022. Anaxyrus boreas. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2022: e.T181488862A197445871. Accessed on 15 December 2022.
- ^ "Anaxyrus boreas. NatureServe Explorer 2.0". explorer.natureserve.org. Retrieved 15 December 2022.
- ^ Frost, Darrel R. (2016). "Anaxyrus boreas (Baird and Girard, 1852)". Amphibian Species of the World: an Online Reference. Version 6.0. American Museum of Natural History. Retrieved 6 February 2016.
- ^ "Anaxyrus boreas". AmphibiaWeb: Information on amphibian biology and conservation. [web application]. Berkeley, California: AmphibiaWeb. 2016. Retrieved 6 February 2016.
- ^ Grismer, L. L. (2002). Amphibians and Reptiles of Baja California. Los Angeles: University of California Press, p. 66, ISBN 0520925203.

