
Back سماك مرتبط بX Arabic X-chromosomale Ichthyose German X-շղթայակցված իխտիոզ Armenian Ittiosi X-linked Italian X연관 어린선 Korean X-связанный ихтиоз Russian
| X-linked ichthyosis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Steroid sulfatase deficiency, X-linked recessive ichthyosis[1] |
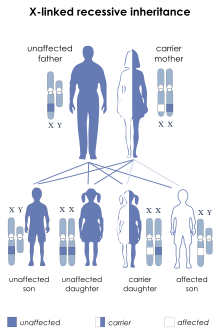 | |
| X-linked recessive inheritance: Affected boys may inherit a deletion or mutation of the STS gene from their mothers | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
X-linked ichthyosis (abbreviated XLI) is a skin condition caused by the hereditary deficiency of the steroid sulfatase (STS) enzyme that affects 1 in 2000 to 1 in 6000 males.[2] XLI manifests with dry, scaly skin[3] and is due to deletions[4][5] or mutations[6] in the STS gene. XLI can also occur in the context of larger deletions causing contiguous gene syndromes.[4] Treatment is largely aimed at alleviating the skin symptoms.[7] The term is from the Ancient Greek 'ichthys' meaning 'fish'.
- ^ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ^ Carlo Gelmetti; Caputo, Ruggero (2002). Pediatric Dermatology and Dermatopathology: A Concise Atlas. T&F STM. p. 160. ISBN 978-1-84184-120-5.
- ^ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): ICHTHYOSIS, X-LINKED - 308100
- ^ a b Ballabio A, Parenti G, Carrozzo R, et al. (1987). "Isolation and characterization of a steroid sulfatase cDNA clone: genomic deletions in patients with X-chromosome-linked ichthyosis". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84 (13): 4519–23. Bibcode:1987PNAS...84.4519B. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.13.4519. PMC 305121. PMID 3474618.
- ^ Bonifas JM, Morley BJ, Oakey RE, Kan YW, Epstein EH (December 1987). "Cloning of a cDNA for steroid sulfatase: frequent occurrence of gene deletions in patients with recessive X chromosome-linked ichthyosis". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84 (24): 9248–51. Bibcode:1987PNAS...84.9248B. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.24.9248. PMC 299730. PMID 3480541.
- ^ Basler E, Grompe M, Parenti G, Yates J, Ballabio A (March 1992). "Identification of point mutations in the steroid sulfatase gene of three patients with X-linked ichthyosis". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 50 (3): 483–91. PMC 1684279. PMID 1539590.
- ^ Ichthyosis, X-Linked at eMedicine: Treatment Section