
Back ثلاثي أكسيد الزينون Arabic زنون تریاوکسید AZB Oxid xenonový Czech Xenon(VI)-oxid German Τριοξείδιο του ξένου Greek تریاکسید زنون Persian Ksenontrioksidi Finnish Trioxyde de xénon French जेनन ट्राइऑक्साइड Hindi Xenon-trioxid Hungarian
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Xenon trioxide
Xenon(VI) oxide | |
| Other names
Xenic anhydride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
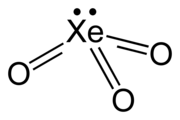
| XeO3 | |
| Molar mass | 179.288 g/mol |
| Appearance | colourless crystalline solid |
| Density | 4.55 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 25 °C (77 °F; 298 K) Violent decomposition |
| Soluble (with reaction) | |
| Structure | |
| trigonal pyramidal (C3v) | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
402 kJ·mol−1[1] |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Xenon tetroxide Xenic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Xenon trioxide is an unstable compound of xenon in its +6 oxidation state. It is a very powerful oxidizing agent, and liberates oxygen from water slowly, accelerated by exposure to sunlight. It is dangerously explosive upon contact with organic materials. When it detonates, it releases xenon and oxygen gas.
- ^ Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A23. ISBN 978-0-618-94690-7.
