
Back بی آی ان ای پی AZB BINAP Czech BINAP German BINAP English BINAP Persian BINAP Finnish BINAP Italian BINAP Japanese BINAP Dutch BINAP Serbo-Croatian
| BINAP | |
| |
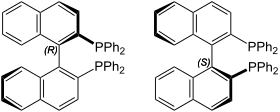
| Atropoisomère R du BINAP (à gauche) et S-BINAP (à droite) | |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | 2,2'-bis(diphénylphosphino)-1,1'-binaphtyle |
| No CAS | |
| No ECHA | 100.114.880 |
| InChI | |
| Apparence | solide blanc |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C44H32P2 [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 622,672 4 ± 0,037 4 g/mol C 84,87 %, H 5,18 %, P 9,95 %, |
| Propriétés physiques | |
| T° fusion | 278 à 282 °C[2] 239 à 241 °C (R)[3] 189 à 193 °C (S)[4] |
| Propriétés optiques | |
| Pouvoir rotatoire | 143,7° (chloroforme, 0,015 g·l-1) (R)[5] –139,1° (chloroforme, 0,015 g·l-1) (S)[5] |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
| modifier |
|
BINAP est l'abréviation du composé organophosphoré 2,2'-bis(diphénylphosphino)-1,1'-binaphtyle. Il s'agit d'un ligand chiral largement utilisé en synthèse organique.
- ↑ Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- ↑ (en) Carl A. Busacca, « Reduction of Tertiary Phosphine Oxides with DIBAL-H », The Journal of Organic Chemistry, vol. 73, no 4, , p. 1524-1531 (DOI 10.1021/jo7024064)
- ↑ (R)-BINAP sur Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ (S)-BINAP sur Sigma-Aldrich
- (en) Christian Müller, « Self-Assembly, Chiroptical Properties, and Host−Guest Chemistry of Chiral Pt−Pt and Pt−Pd Tetranuclear Macrocycles. Circular Dichroism Studies on Neutral Guest Inclusion Phenomena », Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 120, no 38, , p. 9827-9837 (DOI 10.1021/ja9820801)
