[[Category:Lua error in Module:Pagetype at line 175: attempt to call upvalue 'getPageObject' (a nil value). with short description]]
| International Phonetic Alphabet | |
|---|---|
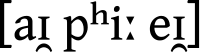 "IPA" in IPA ([aɪ pʰiː eɪ]) | |
| Script type | Alphabet
– partially featural |
Time period | 1888 to present |
| Languages | Used for phonetic and phonemic transcription of any language |
| Related scripts | |
Parent systems | |
| ISO 15924 | |
| ISO 15924 | Template:ISO 15924 code (Template:ISO 15924 number), Template:ISO 15924 name |

The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standardized representation of speech sounds in written form.[1] The IPA is used by lexicographers, foreign language students and teachers, linguists, speech–language pathologists, singers, actors, constructed language creators, and translators.[2][3]
The IPA is designed to represent those qualities of speech that are part of lexical (and, to a limited extent, prosodic) sounds in oral language: phones, phonemes, intonation, and the separation of words and syllables.[1] To represent additional qualities of speech—such as tooth gnashing, lisping, and sounds made with a cleft lip and cleft palate—an extended set of symbols may be used.[2]
Segments are transcribed by one or more IPA symbols of two basic types: letters and diacritics. For example, the sound of the English letter ⟨t⟩ may be transcribed in IPA with a single letter: [t], or with a letter plus diacritics: [t̺ʰ], depending on how precise one wishes to be. Slashes are used to signal phonemic transcription; therefore, /t/ is more abstract than either [t̺ʰ] or [t] and might refer to either, depending on the context and language.[note 1]
Occasionally, letters or diacritics are added, removed, or modified by the International Phonetic Association. As of the most recent change in 2005,[4] there are 107 segmental letters, an indefinitely large number of suprasegmental letters, 44 diacritics (not counting composites), and four extra-lexical prosodic marks in the IPA. Most of these are shown in the current IPA chart, posted below in this article and at the website of the IPA.[5]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 International Phonetic Association (IPA), Handbook.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 MacMahon, Michael K. C. (1996). "Phonetic Notation". In P. T. Daniels. The World's Writing Systems. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 821–846. ISBN 0-19-507993-0. https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780195079937/page/821.
- ↑ Wall, Joan (1989). International Phonetic Alphabet for Singers: A Manual for English and Foreign Language Diction. Pst. ISBN 1-877761-50-8.
- ↑ "IPA: Alphabet". Langsci.ucl.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 10 October 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- ↑ "Full IPA Chart". International Phonetic Association. Retrieved 24 April 2017.
Cite error: <ref> tags exist for a group named "note", but no corresponding <references group="note"/> tag was found
