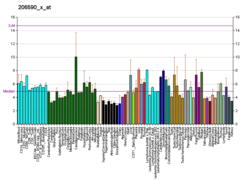
Erro de citação: Etiqueta <ref> inválida; refs sem parâmetro de nome devem ter conteúdo associado
| DRD2 |
|---|
 |
| Estruturas disponíveis |
|---|
| PDB | Pesquisa Human UniProt: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| Lista de códigos id do PDB |
|---|
6CM4 |
|
|
| Identificadores |
|---|
| Nomes alternativos | DRD2 |
|---|
| IDs externos | OMIM: 126450 HomoloGene: 22561 GeneCards: DRD2 |
|---|
|
| Doenças Geneticamente Relacionadas |
|---|
| depressão nervosa[1] |
|
| Targeted by Drug |
|---|
| remoxipride[2] |
| benzquinamide, LP-12, LP-211, LP-44, Ropinirol, Rotigotina, Vilazodona, 7-hydroxy-2-(di-N-propylamino)tetralin, bromocriptina, dopamina, pergolide, pramipexole, quinelorane, quinpirole, sumanirole, apomorfina, aripiprazol, Brexpiprazol, cabergolina, lisurida, piribedil, roxindole, Tergurida, amissulprida, blonanserin, (+)-butaclamol, clorpromazina, clozapina, domperidona, eticlopride, Flupentixol, flufenazina, haloperidol, L-741,626, loxapina, mesoridazine, nafadotride, olanzapina, perospirone, perphenazine, pimozida, pipotiazine, Proclorperazina, promazina, quetiapina, raclopride, risperidona, sertindole, (RS)-sulpiride, levosulpiride, trifluoperazina, ziprasidona, zotepina[3] |
| Ontologia genética |
|---|
| Função molecular | • protein homodimerization activity
• potassium channel regulator activity
• dopamine neurotransmitter receptor activity, coupled via Gi/Go
• identical protein binding
• dopamine neurotransmitter receptor activity
• G protein-coupled receptor activity
• GO:0001948, GO:0016582 ligação a proteínas plasmáticas
• signal transducer activity
• adrenergic receptor activity
• dopamine binding
• signaling receptor binding
• ionotropic glutamate receptor binding
• protein heterodimerization activity
|
|---|
| Componente celular | • GO:0016023 cytoplasmic vesicle
• sperm flagellum
• endocytic vesicle
• Acrossoma
• Espinha dendrítica
• synaptic vesicle membrane
• soma
• membrana plasmática
• dendrito
• ciliary membrane
• axon terminus
• integral component of membrane
• GO:0097483, GO:0097481 postsynaptic density
• membrane
• lateral plasma membrane
• axónio
• intracellular anatomical structure
• non-motile cilium
• integral component of plasma membrane
• dopaminergic synapse
• glutamatergic synapse
• GABA-ergic synapse
• integral component of postsynaptic membrane
• integral component of presynaptic membrane
|
|---|
| Processo biológico | • negative regulation of cell population proliferation
• temperature homeostasis
• adenylate cyclase-inhibiting dopamine receptor signaling pathway
• adenohypophysis development
• circadian regulation of gene expression
• response to toxic substance
• regulation of dopamine secretion
• response to cocaine
• response to amphetamine
• sensory perception of smell
• locomotory behavior
• positive regulation of urine volume
• response to ethanol
• axonogenesis
• response to inactivity
• phospholipase C-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway
• modulation of chemical synaptic transmission
• grooming behavior
• negative regulation of protein kinase B signaling
• associative learning
• positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration involved in phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled signaling pathway
• regulation of dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission
• regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic
• positive regulation of dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission
• GO:0072468 transdução de sinal
• Via de sinalização Wnt
• adult walking behavior
• branching morphogenesis of a nerve
• negative regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration
• negative regulation of innate immune response
• regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity
• acid secretion
• feeding behavior
• positive regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway
• response to axon injury
• striatum development
• synaptic transmission, dopaminergic
• nervous system process involved in regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure
• movimento peristáltico
• regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity
• activation of protein kinase activity
• positive regulation of growth hormone secretion
• regulation of sodium ion transport
• forebrain development
• response to light stimulus
• orbitofrontal cortex development
• prepulse inhibition
• response to morphine
• response to iron ion
• positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade
• memória de longo prazo
• positive regulation of renal sodium excretion
• negative regulation of insulin secretion
• neuron-neuron synaptic transmission
• GO:0007243 intracellular signal transduction
• auditory behavior
• behavioral response to ethanol
• regulation of heart rate
• adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway
• positive regulation of cytokinesis
• regulation of potassium ion transport
• pigmentation
• cellular calcium ion homeostasis
• dopamine metabolic process
• response to nicotine
• regulation of MAPK cascade
• response to histamine
• negative regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic
• response to hypoxia
• negative regulation of circadian sleep/wake cycle, sleep
• negative regulation of protein secretion
• Sinaptogênese
• regulation of locomotion involved in locomotory behavior
• dopamine receptor signaling pathway
• negative regulation of dopamine receptor signaling pathway
• startle response
• positive regulation of receptor internalization
• GO:0034613 protein localization
• arachidonic acid secretion
• GO:0003257, GO:0010735, GO:1901228, GO:1900622, GO:1904488 positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
• G protein-coupled receptor internalization
• positive regulation of multicellular organism growth
• positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation
• negative regulation of dopamine secretion
• adult behavior
• cerebral cortex GABAergic interneuron migration
• regulation of synapse structural plasticity
• adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway
• visual learning
• negative regulation of cell migration
• behavioral response to cocaine
• positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation
• negative regulation of blood pressure
• release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol
• negative regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel activity
• G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway
• negative regulation of adenylate cyclase activity
• potencial pós-sináptico excitatório
• GO:0033128 negative regulation of protein phosphorylation
• autofagia
• positive regulation of neurogenesis
• negative regulation of cell death
• drinking behavior
• adrenergic receptor signaling pathway
• regulation of neurotransmitter uptake
• postsynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission
• regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis
|
|---|
| Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
|
|
| Wikidata |
|
O receptor D2 de dopamina, também conhecido por D2R, é uma proteína que, em seres humanos, é codificada pelo gene DRD2.
Não só é o principal receptor da maioria dos medicamentos antipsicóticos, como foi através destes medicamentos que foi identificado em 1975. Na busca pelo mecanismo fisiopatológico da psicose, a equipe procurou identificar os locais que se ligavam ao medicamento antipsicótico haloperidol.[5]
Este gene codifica o subtipo D2 dos receptores de dopamina. Este receptor acoplado à proteína G inibe a actividade da adenilato ciclase, sendo portanto associado à variante Gi. Uma mutação missence neste gene causa distonia mioclónica; outras mutações têm sido associadas com a esquizofrenia.[6]
O splicing alternativo deste gene resulta em duas variantes de trancriptos que codificam diferentes isoformas[7], D2S (D2-short) e D2L (D2-long).[5][8]
A variante longa (D2L) funciona como um tradicional receptor pós-sináptico. Já a versão curta (D2S) trata-se de um receptor pré-sináptico, que funciona como um autoreceptor, ou seja, pode aumentar ou reduzir a quantidade de dopamina libertada para o espaço extracelular, dependendo da quantidade presente.[8]