
Back خلية بائية Arabic B-клетка Bulgarian বি কোষ Bengali/Bangla B-ćelija BS Limfòcit B Catalan B-lymfocyt Czech B-celle Danish B-Lymphozyt German ބީ ލިމްފަސައިޓް DV Β κύτταρα Greek
| B cell | |
|---|---|
 The cells of the immune system form cells that remember the pathogen for future infections. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | lymphocytus B |
| MeSH | D001402 |
| FMA | 62869 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
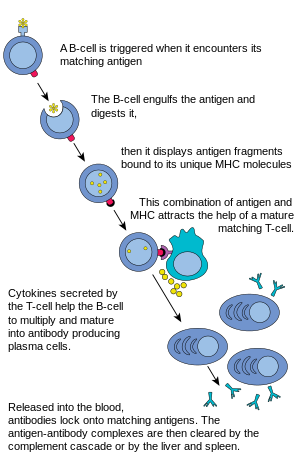
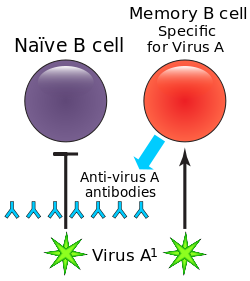
B cells are lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell. Once the B cell is activated, it turns into a plasma cell,[a] and starts producing antibodies. They are a vital part of the adaptive immune system. They have a protein on the B cell's outer surface known as a 'B cell receptor'. This allows a B cell to bind to a specific antigen.
The main functions of B cells are:
- to make antibodies against antigens,
- to perform the role of antigen-presenting cells (APCs),
- to develop into memory B cells after activation by antigen interaction.
Recently, a new, suppressive function of B cells has been discovered.[1]
In mammals, immature B cells are formed in the bone marrow, hence their name.[2]
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ↑ Mauri, Claudia; Bosma, Anneleen (2012). "Immune regulatory function of B Cells". Annual Review of Immunology. 30: 221–41. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-074934. PMID 22224776.
- ↑ Alberts B. et al 2002. Molecular biology of the cell. Garland Science: New York, pg 1367.