
Back Baikalmeer Afrikaans Baikalsee ALS ባይካል ሐይቅ Amharic Laco Baikal AN بحيرة بايكال Arabic ضاية بايكال ARY بحيرة بايكال ARZ বৈকাল হ্ৰদ Assamese Llagu Baikal AST Baykal Azerbaijani
| Lake Baikal | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Coordinates | 53°30′N 108°0′E / 53.500°N 108.000°E |
| Lake type | Continental rift lake |
| Primary inflows | Selenge, Barguzin, Upper Angara |
| Primary outflows | Angara |
| Catchment area | 560,000 km2 (216,000 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | Russia and Mongolia |
| Max. length | 636 km (395 mi) |
| Max. width | 79 km (49 mi) |
| Surface area | 31,722 km2 (12,248 sq mi)[1] |
| Average depth | 744.4 m (2,442 ft)[1] |
| Max. depth | 1,642 m (5,387 ft)[1] |
| Water volume | 23,615.39 km3 (5,700 cu mi)[1] |
| Residence time | 330 years[2] |
| Shore length1 | 2,100 km (1,300 mi) |
| Surface elevation | 455.5 m (1,494 ft) |
| Frozen | January–May |
| Islands | 27 (Olkhon) |
| Settlements | Irkutsk |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
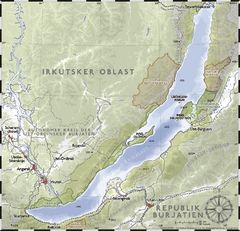
Lake Baikal is a huge lake in Siberia, Russia. It is the biggest fresh water reservoir in the world. The lake is near Irkutsk.
Baikal is about 636 km (395 mi) long. It is 20 to 80 km (12 to 50 mi) wide. At its deepest point, it is 1,700 m (5,600 ft) deep. It is the deepest lake on Earth.[3][4] The lake is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It holds about 20% of the world's unfrozen surface fresh water.[5]
The lake has unique fish. It is home to more than 1,700 species of plants and animals. Two-thirds of them can be found nowhere else.[6]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "A new bathymetric map of Lake Baikal. MORPHOMETRIC DATA. INTAS Project 99-1669.Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium; Consolidated Research Group on Marine Geosciences (CRG-MG), University of Barcelona, Spain; Limnological Institute of the Siberian Division of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Irkutsk, Russian Federation; State Science Research Navigation-Hydrographic Institute of the Ministry of Defense, St.Petersburg, Russian Federation". Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium. Archived from the original on 25 December 2018. Retrieved 9 July 2009.
- ↑ M.A. Grachev. "On the present state of the ecological system of lake Baikal". Lymnological Institute, Siberian Division of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Archived from the original on 25 December 2018. Retrieved 9 July 2009.
- ↑ "About Lake Baikal=--- details from the Encyclopedia". irkutsk.org. Retrieved 5 August 2010.
- ↑ "Lake Baikal - UNESCO World Heritage Centre". whc.unesco.org. Retrieved 5 August 2010.
- ↑ "Lake Baikal: the great blue eye of Siberia". CNN. Archived from the original on 11 October 2006. Retrieved 21 October 2006.
- ↑ "Russia". Britannica Student Encyclopedia. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 2007. Archived from the original on 8 August 2007. Retrieved 3 July 2007.