
Back Алаҭын бызшәа Abkhazian Latyn Afrikaans Lateinische Sprache ALS ሮማይስጥ Amharic Latín AN Læden ANG Latin ANN लैटिन भाषा ANP اللغة اللاتينية Arabic ܠܫܢܐ ܠܐܛܝܢܝܐ ARC
| Latin | |
|---|---|
| lingua latīna | |
 Latin inscription, in the Colosseum | |
| Pronunciation | [laˈtiːna] |
| Native to | |
| Ethnicity | Latins |
| Era | Vulgar Latin developed into the Romance languages, 6th to 9th centuries; the formal language continued as the scholarly lingua franca of Catholic countries and medieval Europe and as the liturgical language of the Catholic Church. |
| Latin alphabet | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Regulated by |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | la |
| ISO 639-2 | lat |
| ISO 639-3 | lat |
| Glottolog | impe1234lati1261 |
| Linguasphere | 51-AAB-aa to 51-AAB-ac |
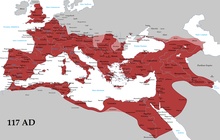 Map indicating the greatest extent of the Roman Empire under Emperor Trojan (c. 117 AD) and the area governed by Latin speakers (dark red). Many languages other than Latin were spoken within the empire. | |
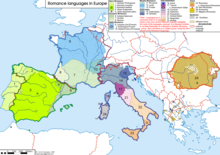 Range of the Romance languages, the modern descendants of Latin, in Europe. | |
Latin is an Italic language that was developed in Ancient Rome. Short Latin texts have been found from about the 5th century BC and longer texts from about the 3rd century BC.
- ↑ "Schools". Britannica (1911 ed.).