
Back Oktaan Afrikaans أوكتان Arabic Oktan Azerbaijani اوکتان AZB Октан Bulgarian অক্টেন Bengali/Bangla Oktan BS Octà Catalan Oktan Czech Октанъ CU
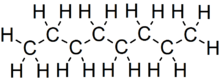
| ||
| ||
| ||
| Names | ||
|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Octane[1]
| ||
| Identifiers | ||
3D model (JSmol)
|
||
| 3DMet | ||
| Beilstein Reference | 1696875 | |
| ChEBI | ||
| ChEMBL | ||
| ChemSpider | ||
| DrugBank | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.539 | |
| EC Number |
| |
| Gmelin Reference | 82412 | |
| KEGG | ||
| MeSH | octane | |
PubChem CID
|
||
| RTECS number |
| |
| UN number | 1262 | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
||
| ||
| Properties | ||
| C8H18 | ||
| Molar mass | 114.23 g·mol−1 | |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | |
| Odor | Gasoline-like[2] | |
| Density | 0.703 g cm−3 | |
| Melting point | −57.1 to −56.6 °C; −70.9 to −69.8 °F; 216.0 to 216.6 K | |
| Boiling point | 125.1 to 126.1 °C; 257.1 to 258.9 °F; 398.2 to 399.2 K | |
| 0.007 mg dm−3 (at 20 °C) | ||
| log P | 4.783 | |
| Vapor pressure | 1.47 kPa (at 20.0 °C) | |
| kH | 29 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 | |
| Conjugate acid | Octonium | |
| -96.63·10−6 cm3/mol | ||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.398 | |
| Viscosity | 542 μPa s (at 20 °C) | |
| Thermochemistry | ||
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH |
−252.1–−248.5 kJ mol−1 | |
| Std enthalpy of combustion ΔcH |
−5.53–−5.33 MJ mol−1 | |
| Standard molar entropy S |
361.20 J K−1 mol−1 | |
| Specific heat capacity, C | 255.68 J K−1 mol−1 | |
| Hazards | ||
| NFPA 704 |
| |
| Explosive limits | 0.96–6.5% | |
| U.S. Permissible exposure limit (PEL) |
TWA 500 ppm (2350 mg/m3)[2] | |
| Related compounds | ||
| Related {{{label}}} | {{{value}}} | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | ||
| Infobox references | ||
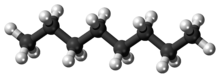
Octane is an organic compound with the chemical formula C
8H
18. It is an alkane with eight carbon atoms. It is commonly used in fuel. It is the most important part of gasoline, because it is the part that lets out most of the energy that comes from gasoline when it is burned. A high octane fuel will be better than a low octane fuel.
- ↑ "octane - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2004. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 6 January 2012.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0470". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
