
Back محفز (علم الوراثة) Arabic Promotor (genetika) BS Promotor Catalan پڕۆمۆتەر CKB Promotor (genetika) Czech Promotor (biologi) Danish Promotor (Genetik) German Υποκινητής (βιολογία) Greek Promoter (genetics) English Promotoro Esperanto
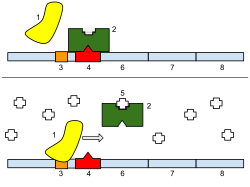
Top: The gene is turned off. There is no lactose to inhibit the repressor, so the repressor binds to the operator. This stops the RNA polymerase from binding to the promoter and making lactase.
Bottom: The gene is turned on. Lactose inhibits the repressor. This allows the RNA polymerase to bind with the promoter, and express the genes. The genes now synthesize lactase. Eventually, the lactase will digest all of the lactose, until there is none to bind to the repressor. The repressor will then bind to the operator, stopping the manufacture of lactase.
In genetics, a promoter is a section of DNA which starts the transcription of a gene.
Promoters are near the genes they transcribe. They are on the same strand of DNA and are 'upstream'.
Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.[1]
- ↑ "Analysis of biological networks: transcriptional networks - promoter sequence analysis" (PDF). Tel Aviv University. Retrieved 30 December 2012.