
Back Skynprivaatnetwerk Afrikaans شبكة خاصة افتراضية Arabic Rede privada virtual AST VPN Azerbaijani VPN Byelorussian VPN BE-X-OLD Виртуална частна мрежа Bulgarian वर्चुअल प्राइवेट नेटवर्क Bihari ভার্চুয়াল প্রাইভেট নেটওয়ার্ক Bengali/Bangla Virtualna privatna mreža BS
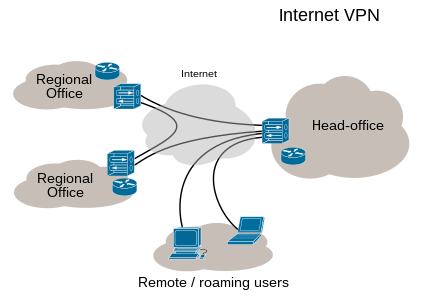
A virtual private network, or VPN is a set of technologies which are used to link computers to create a private network. Another network is used to carry the data, which is encrypted. The carrier network will see the packets of data which it routes. To the users of the VPN, it will look like the computers were directly connected to each other.
The VPN model can guarantee the following:
- Confidentiality: The carrier network will route the data, but it will be unable to decrypt it.
- Sender authentication: People need to authenticate themselves, to be able to use the network.
- Message integrity: Messages transported across the network cannot be changed easily while they are in transport. When a message was changed, it is possible to detect this.
In a business context, VPNs are often used to connect different office locations or to allow people working from outside the company network to access its resources. VPNs are a crucial tool for securing sensitive data and enabling secure remote access for employees, especially with the rise of remote work. Businesses are turning to VPNs to create a secure and encrypted connection for employees accessing company data from remote locations, ensuring that work websites that cannot be accessed on the normal internet can be securely accessed. Additionally, VPNs provide a safe and encrypted connection for employees to access company resources, protecting sensitive data from cyber threats.
Similarly, the encryption process allows VPNs to offer anonymity by hiding the user and making it very hard for anyone to track them. As a result, VPNs help make one's online activities on the web anonymous and undecipherable.
VPNs are often used to access websites that are blocked in some countries, like China.[1] Many people also use a VPN to protect their internet activity while using public WiFi.
VPNs can also be used to connect corporate offices to the larger branch offices, also known as site-to-site VPN. This is because direct network connections are impractical between offices that are physically distant. Common VPN protocols include OpenVPN, Cisco AnyConnect, and IPsec.
- ↑ Yang, Stephanie. "China Has Escalated Internet Censorship To A New Level". Business Insider.