Back Joego-Slawië Afrikaans Jugoslawien ALS ዩጎስላቪያ Amharic Geugoslafia ANG يوغوسلافيا Arabic يوݣوسلاڤيا ARY يوجوسلاڤيا ARZ Yugoslavia AST Yuqoslaviya Azerbaijani Югославия Bashkir

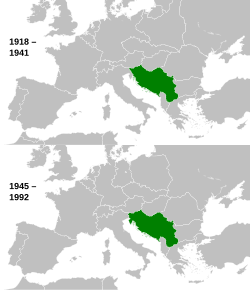
Yugoslavia was a country in Europe that lay mostly in the Balkan Peninsula. It existed in one of three forms from 1918 to 1992 [source?].[1] Yugoslavia means “land of the south Slavs”. The name comes from people who left Poland, which was to the north of Yugoslavia. Yugoslavia contained a wide range of different ethnic groups that spoke different languages, used different alphabets and worshipped different religions. These included Serbs, Croats, Bosniaks, Slovenes, Herzegovinians, Montenegrins, Macedonians and Albanians.
From 1918 until 1928 it was called the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. From 1928 until World War II it was the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. After WWII it was renamed the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia with six republics, 2 autonomous provinces: Bosnia-Herzegovina, Croatia, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Slovenia and two autonomous provinces in Serbia: Vojvodina in the north, and Kosovo, next to Albania.
In 1991, came the independence of Slovenia, Croatia, in 1992, North Macedonia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, causing the end of the country. Serbia and Montenegro, were the last two republics in the Socialist Yugoslavia. In 1992, they formed a new Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY) which ended in 2006 with Montenegro declaring independence.
- ↑ Ramet, Sabrina: The Three Yugoslavia: State-building and Legitimation, 1918–2003. Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 2006