
Back انتخابات الرئاسة الأمريكية 1804 Arabic ھەڵبژاردنی سەرۆکایەتیی ویلایەتە یەکگرتووەکانی ئەمریکا (١٨٠٤) CKB Volby prezidenta USA 1804 Czech Præsidentvalget i USA 1804 Danish Präsidentschaftswahl in den Vereinigten Staaten 1804 German Elecciones presidenciales de Estados Unidos de 1804 Spanish انتخابات ریاستجمهوری ایالات متحده آمریکا (۱۸۰۴) Persian Yhdysvaltain presidentinvaalit 1804 Finnish Élection présidentielle américaine de 1804 French הבחירות לנשיאות ארצות הברית 1804 HE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
176 members of the Electoral College 89 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 23.8%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
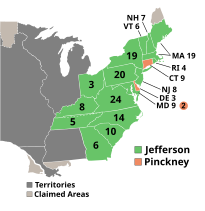 Presidential election results map. Green denotes states won by Jefferson and Light Orange denotes states won by Pinckney. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes cast by each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Presidential elections were held in the United States from November 2 to December 5, 1804. Incumbent Democratic-Republican president Thomas Jefferson defeated Federalist Charles Cotesworth Pinckney of South Carolina. It was the first presidential election conducted following the ratification of the Twelfth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which reformed procedures for electing presidents and vice presidents.
Jefferson was renominated by his party's congressional nominating caucus without opposition, and the party nominated Governor George Clinton of New York to replace Aaron Burr as Jefferson's running mate. With former president John Adams in retirement, the Federalists turned to Pinckney, a former ambassador and Revolutionary War hero who had been Adams's running mate in the 1800 election.
Though Jefferson had only narrowly defeated Adams in 1800, he was widely popular due to the Louisiana Purchase and a strong economy. He carried almost every state, including most states in the Federalist stronghold of New England.
- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.

