
Back سمين ضفدعي Arabic Batracotoxina Catalan Batrachotoxin Czech Batrachotoxin German Batracotoxina Spanish باتراکوتوکسین Persian Batrakotoksiinit Finnish Batrachotoxine French Batracotossina Italian バトラコトキシン Japanese
 Skeletal formula of batrachotoxin
| |
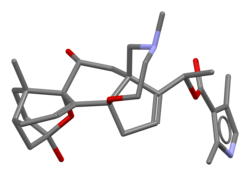 Stick model of batrachotoxin based on the crystal structure of batrachotoxinin A O-p-bromobenzoate[1]
| |
 Ball-and-stick model of batrachotoxin, as above[1]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
3α,9α-epoxy-14β,18-(2′-oxyethyl-N-methylamino)-5β-pregna-7,16-diene-3β,11α,20α-triol 20α-2,4-dimethylpyrrole-3-carboxylate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C31H42N2O6 | |
| Molar mass | 538.685 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.304 g/mL[2] |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Highly toxic |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
2 μg/kg (mouse, sub-cutaneous) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Batrachotoxin (BTX) is an extremely potent cardiotoxic and neurotoxic steroidal alkaloid found in certain species of beetles, birds, and frogs. The name is from the Greek word βάτραχος, bátrachos, 'frog'.[3] Structurally-related chemical compounds are often referred to collectively as batrachotoxins. In certain frogs, this alkaloid is present mostly on the skin. Such frogs are among those used for poisoning darts. Batrachotoxin binds to and irreversibly opens the sodium channels of nerve cells and prevents them from closing, resulting in paralysis and death. No antidote is known.
- ^ a b Karle, I. L.; Karle, J. (1969). "The structural formula and crystal structure of the O-p-bromobenzoate derivative of batrachotoxinin A, C31H38NO6Br, a frog venom and steroidal alkaloid". Acta Crystallographica Section B. 25 (3): 428–434. Bibcode:1969AcCrB..25..428K. doi:10.1107/S056774086900238X. PMID 5820223. S2CID 28609553.
- ^ Daly, J. W.; Witkop, B.; Bommer, P.; Biemann, K. (January 1965). "Batrachotoxin. The Active Principle of the Colombian Arrow Poison Frog, Phyllobates bicolor". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 87 (1): 124–126. Bibcode:1965JAChS..87..124D. doi:10.1021/ja01079a026. PMID 5826972.
- ^ The Merck Index. Entry 1009. p. 167.