
Back قانون مقارن Arabic Derechu comparáu AST Müqayisəli hüquq Azerbaijani Сравнително право Bulgarian Komparativ ret Danish Vergleichende Rechtswissenschaft German Συγκριτικό δίκαιο Greek Derecho comparado Spanish Võrdlev õigusteadus Estonian حقوق تطبیقی Persian
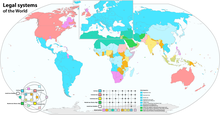
Comparative law is the study of differences and similarities between the law and legal systems of different countries. More specifically, it involves the study of the different legal systems (or "families") in existence around the world, including common law, civil law, socialist law, Canon law, Jewish Law, Islamic law, Hindu law, and Chinese law. It includes the description and analysis of foreign legal systems, even where no explicit comparison is undertaken. The importance of comparative law has increased enormously in the present age of internationalism and economic globalization.