Back Delta Sagittae AST Delta Sagittae Spanish Delta Sagittae French Delta Sagittae Italian Delta Sagittae Portuguese Delta Sagittae Swedish 左旗三 Chinese
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Sagitta |
| Right ascension | 19h 47m 23.26653s[1] |
| Declination | +18° 32′ 03.5203″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +3.82[2](3.91[3]/ 6.64)[4] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M2II + B9.5V[4] |
| U−B color index | +0.98[5] |
| B−V color index | +1.40[5] |
| Variable type | LB?[6] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 2.5 ± 0.9[7] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: -6.514[1] mas/yr Dec.: 0.849[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 5.9674 ± 0.2597 mas[8] |
| Distance | 550 ± 20 ly (168 ± 7 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −2.58[9] |
| Orbit[4] | |
| Period (P) | 10.15[10] yr |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 0.051″ |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.453[10] |
| Inclination (i) | 140.0° |
| Longitude of the node (Ω) | 170.2° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 1979.93 |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 257.7° |
| Details | |
| δ Sge A | |
| Mass | 4.073[10] M☉ |
| Radius | 223 – 267[10] R☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 0.74 ± 0.10[11] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,660±170[12] K |
| δ Sge B | |
| Mass | 3.611[10] M☉ |
| Radius | 3.3 – 4.7[10] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 63[4] L☉ |
| Temperature | 10000[4] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
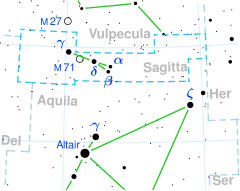
Delta Sagittae (Delta Sge, δ Sagittae, δ Sge) is a binary star in the constellation of Sagitta, with an apparent magnitude of +3.68. The primary component is a red M-type bright giant, and the secondary is a B-type main-sequence star.[2] It is approximately 430 light years from Earth, based on its Gaia Data Release 2 parallax.[1]
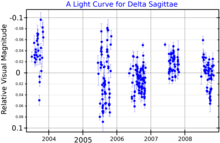
Delta Sagittae is a spectroscopic binary with a composite spectrum, meaning that light from both stars can be detected. It has an orbital period of about 10 years and an eccentricity of about 0.44.[4] It is also a variable star, with its brightness changing between a maximum of magnitude 3.75 and a minimum of 3.83 in an unpredictable way.[6]
Delta Sagittae is moving through the Galaxy at a speed of 9.8 km/s relative to the Sun. Its projected Galactic orbit carries it between 23,800 and 35,300 light years from the center of the Galaxy.[14][better source needed]
- ^ a b c d e Cite error: The named reference
DR2was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
SIMBADwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
calcwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f Cite error: The named reference
Eatonwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
EgUBVwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
gcvswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
GCRVwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Gaia3was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Anderson2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f Eggleton, Peter P.; Yakut, Kadri (2017). "Models for 60 double-lined binaries containing giants". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 468 (3): 3533–3556. arXiv:1611.05041. doi:10.1093/mnras/stx598.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Schroederwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
messiniowas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Taburwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
astrostudiowas invoked but never defined (see the help page).