Back ثنائي كلورو ثنائي فلورو الميثان Arabic دیکولورودیفلوئورومتان AZB Diclorodifluorometà Catalan Dichlordifluormethan Czech Dichlordifluormethan German Διφθοροδιχλωρομεθάνιο Greek دیکلرودیفلوئورومتان Persian Difluoridikloorimetaani Finnish Dichlorodifluorométhane French Difluor-diklórmetán Hungarian
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dichlorodi(fluoro)methane | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.813 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| E number | E940 (glazing agents, ...) | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1028 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
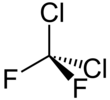
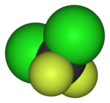
| CCl2F2 | |||
| Molar mass | 120.91 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Odor | ether-like at very high concentrations | ||
| Density | 1.486 g/cm3 (−29.8 °C (−21.6 °F)) | ||
| Melting point | −157.7 °C (−251.9 °F; 115.5 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −29.8 °C (−21.6 °F; 243.3 K) | ||
| 0.286 g/L at 20 °C (68 °F) | |||
| Solubility in alcohol, ether, benzene, acetic acid | Soluble | ||
| log P | 2.16 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 568 kPa (20 °C (68 °F)) | ||
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
0.0025 mol kg−1 bar−1 | ||
| −52.2·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Thermal conductivity | 0.0097 W/(m·K) (300 K)[1] | ||
| Structure | |||
| Tetrahedral | |||
| 0.51 D[2] | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||

| |||
| Warning | |||
| H336, H420 | |||
| P261, P271, P304+P340, P319, P403+P233, P405, P410+P403, P501, P502 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | Non-flammable[3] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
760,000 ppm (mouse, 30 min) 800,000 ppm (rabbit, 30 min) 800,000 ppm (guinea pig, 30 min) 600,000 ppm (rat, 2 h)[4] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1000 ppm (4950 mg/m3)[3] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 1000 ppm (4950 mg/m3)[3] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
15000 ppm[3] | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Dichlorodifluoromethane (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Dichlorodifluoromethane (R-12) is a colorless gas popularly known by the genericized brand name Freon (as Freon-12). It is a chlorofluorocarbon halomethane (CFC) used as a refrigerant and aerosol spray propellant. In compliance with the Montreal Protocol, its manufacture was banned in developed countries (non-article 5 countries) in 1996, and in developing countries (Article 5 countries) in 2010 out of concerns about its damaging effect on the ozone layer.[5] Its only allowed usage is as a fire retardant in submarines and aircraft. It is soluble in many organic solvents. R-12 cylinders are colored white.
- ^ Touloukian, Y. S., Liley, P. E., and Saxena, S. C. Thermophysical properties of matter – the TPRC data series. Volume 3. Thermal conductivity – nonmetallic liquids and gases. Data book. 1970.
- ^ Khristenko, Sergei V.; Maslov, Alexander I. and Viatcheslav P. Shevelko; Molecules and Their Spectroscopic Properties, p. 74 ISBN 3642719481.
- ^ a b c d NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0192". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Dichlorodifluoromethane". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "1:Update on Ozone-Depleting Substances (ODSs) and Other Gases of Interest to the Montreal Protocol". Scientific assessment of ozone depletion: 2018 (PDF) (Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project–Report No. 58 ed.). Geneva, Switzerland: World Meteorological Organization. 2018. p. 1.10. ISBN 978-1-7329317-1-8. Retrieved 22 November 2020.