
Back الاتجاهية (علم الأحياء الجزيئي) Arabic Usmjerenost (genetika) BS Direccionalitat (biologia molecular) Catalan Direkcionalita Czech Direccionalidad Spanish جهتگیری (زیستشناسی مولکولی) Persian Sens 5' vers 3' French Direccionalidade (bioloxía molecular) Galician כיווניות (ביולוגיה) HE Senso (biologia molecolare) Italian
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2023) |
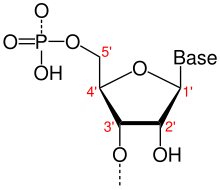
Directionality, in molecular biology and biochemistry, is the end-to-end chemical orientation of a single strand of nucleic acid. In a single strand of DNA or RNA, the chemical convention of naming carbon atoms in the nucleotide pentose-sugar-ring means that there will be a 5′ end (usually pronounced "five-prime end"), which frequently contains a phosphate group attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose ring, and a 3′ end (usually pronounced "three-prime end"), which typically is unmodified from the ribose -OH substituent. In a DNA double helix, the strands run in opposite directions to permit base pairing between them, which is essential for replication or transcription of the encoded information.
Nucleic acids can only be synthesized in vivo in the 5′-to-3′ direction, as the polymerases that assemble various types of new strands generally rely on the energy produced by breaking nucleoside triphosphate bonds to attach new nucleoside monophosphates to the 3′-hydroxyl (−OH) group, via a phosphodiester bond. The relative positions of structures along strands of nucleic acid, including genes and various protein binding sites, are usually noted as being either upstream (towards the 5′-end) or downstream (towards the 3′-end). (See also upstream and downstream.)
Directionality is related to, but different from, sense. Transcription of single-stranded RNA from a double-stranded DNA template requires the selection of one strand of the DNA template as the template strand that directly interacts with the nascent RNA due to complementary sequence. The other strand is not copied directly, but necessarily its sequence will be similar to that of the RNA. Transcription initiation sites generally occur on both strands of an organism's DNA, and specify the location, direction, and circumstances under which transcription will occur. If the transcript encodes one or (rarely) more proteins, translation of each protein by the ribosome will proceed in a 5′-to-3′ direction, and will extend the protein from its N-terminus toward its C-terminus. For example, in a typical gene a start codon (5′-ATG-3′) is a DNA sequence within the sense strand. Transcription begins at an upstream site (relative to the sense strand), and as it proceeds through the region it copies the 3′-TAC-5′ from the template strand to produce 5′-AUG-3′ within a messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA is scanned by the ribosome from the 5′ end, where the start codon directs the incorporation of a methionine (bacteria, mitochondria, and plastids use N-formylmethionine instead) at the N terminus of the protein. By convention, single strands of DNA and RNA sequences are written in a 5′-to-3′ direction except as needed to illustrate the pattern of base pairing.