
Back سخانات مياه التغذية Arabic Oberflächenvorwärmer German دستگاه گرمکننده تغذیه آب Persian Syöttöveden esilämmitin Finnish Экономайзер (энергетика) Russian
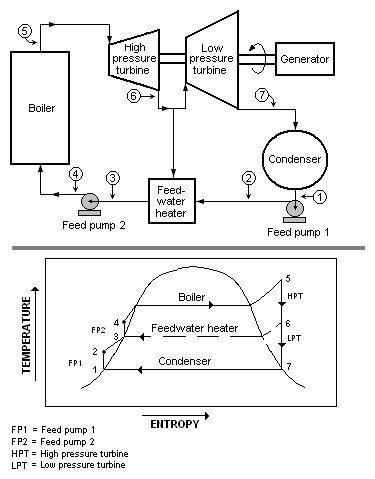
A feedwater heater is a power plant component used to pre-heat water delivered to a steam generating boiler.[1][2][3] Preheating the feedwater reduces the irreversibilities involved in steam generation and therefore improves the thermodynamic efficiency of the system.[4] This reduces plant operating costs and also helps to avoid thermal shock to the boiler metal when the feedwater is introduced back into the steam cycle.
In a steam power plant (usually modeled as a modified Rankine cycle), feedwater heaters allow the feedwater to be brought up to the saturation temperature very gradually. This minimizes the inevitable irreversibilities associated with heat transfer to the working fluid (water). See the article on the second law of thermodynamics for a further discussion of such irreversibilities.
- ^ British Electricity International (1991). Modern Power Station Practice: incorporating modern power system practice (3rd Edition (12 volume set) ed.). Pergamon. ISBN 0-08-040510-X.
- ^ Babcock & Wilcox Co. (2005). Steam: Its Generation and Use (41st ed.). ISBN 0-9634570-0-4.
- ^ Thomas C. Elliott, Kao Chen, Robert Swanekamp (coauthors) (1997). Standard Handbook of Powerplant Engineering (2nd ed.). McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 0-07-019435-1.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Fundamentals of Steam Power Archived 2007-04-22 at the Wayback Machine by Kenneth Weston, University of Tulsa