
Back Homofoon Afrikaans اشتراك لفظي تلفظي Arabic সমধ্বনি Assamese Амафон Byelorussian Амафон BE-X-OLD Омофон Bulgarian Heñvelsonerezh Breton Homofon Czech Homofon Danish Homophon German
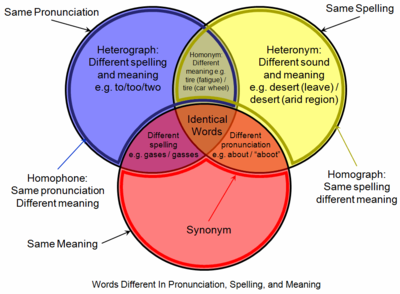
A homophone (/ˈhɒməfoʊn, ˈhoʊmə-/) is a word that is pronounced the same as another word but differs in meaning or in spelling. The two words may be spelled the same, for example rose (flower) and rose (past tense of "rise"), or spelled differently, as in rain, reign, and rein. The term homophone sometimes applies to units longer or shorter than words, for example a phrase, letter, or groups of letters which are pronounced the same as a counterpart. Any unit with this property is said to be homophonous (/həˈmɒfənəs/).
Homophones that are spelled the same are both homographs and homonyms. For example, the word read, in "He is well read" and in "Yesterday, I read that book".[a]
Homophones that are spelled differently are also called heterographs, e.g. to, too, and two.
| Part of a series on |
| Linguistics |
|---|
|
|
- ^ "Homonym". Random House Unabridged Dictionary. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016 – via Dictionary.com.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).