Back Мексика Abkhazian Mèksiko ACE Мексикэ ADY Meksiko Afrikaans Mexiko ALS Мексика ALT ሜክሲኮ Amharic Mexico AMI Mexico AN Mexico ANG
United Mexican States Estados Unidos Mexicanos (Spanish) | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: Himno Nacional Mexicano (English: Mexican National Anthem) | |
| Capital and largest city | Mexico City 19°26′N 99°8′W / 19.433°N 99.133°W |
| Official languages | Spanish (de facto) None (de jure) |
| Co-official languages | |
| Ethnic groups | See below |
| Religion (2020)[1] |
|
| Demonym(s) | Mexican |
| Government | Federal presidential republic[2] |
| Claudia Sheinbaum | |
| Gerardo Fernández Noroña | |
| Sergio Gutiérrez Luna | |
| Norma Lucía Piña Hernández | |
| Legislature | Congress |
| Senate | |
| Chamber of Deputies | |
| Independence from Spain | |
| 16 September 1810 | |
• Declared | 27 September 1821 |
| 28 December 1836 | |
| 4 October 1824 | |
| 5 February 1857 | |
| 5 February 1917 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,972,550 km2 (761,610 sq mi) (13th) |
• Water (%) | 1.58 (as of 2015)[3] |
| Population | |
• 2025 estimate | |
• 2020 census | 126,014,024[5] |
• Density | 61/km2 (158.0/sq mi) (142nd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2025 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2025 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2022) | medium inequality |
| HDI (2023) | high (77th) |
| Currency | Mexican peso (MXN) |
| Time zone | UTC−8 to −5 (See Time in Mexico) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC−7 to −5 (varies) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Drives on | Right |
| Calling code | +52 |
| ISO 3166 code | MX |
| Internet TLD | .mx |
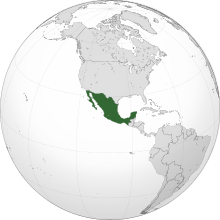
Mexico,[a][b] officially the United Mexican States,[c] is a country in the southern portion of North America. Covering 1,972,550 km2 (761,610 sq mi),[12] it is the world's 13th largest country by area; with a population of over 130 million, it is the 10th most populous country and has the most Spanish speakers in the world.[1] Mexico is a constitutional republic comprising 31 states and Mexico City, its capital and largest city, which is among the world's most populous metropolitan areas. The country borders the United States to the north; as well as Guatemala and Belize to the southeast. It has maritime borders with the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Caribbean Sea to the southeast, and the Gulf of Mexico to the east.[13]
Human presence in Pre-Columbian Mexico dates back to 8,000 BC as one of six cradles of civilization. Mesoamerica hosted civilizations including the Olmec, Maya, Zapotec, Teotihuacan, and Purepecha. Aztec domination of the area preceded Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, which established the colony of New Spain centered in the former capital, Tenochtitlan (now Mexico City).[14] The Mexican War of Independence in the early 19th century was followed by political and socioeconomic upheaval. The Mexican–American War resulted in significant territorial losses in 1848.[15] Liberal reforms introduced in the Constitution of 1857 prompted domestic conflict, French intervention, and the establishment of an Empire, countered by the Republican resistance led by Benito Juárez. The rise of Porfirio Díaz's dictatorship in the 19th century[16] sparked the Mexican Revolution in 1910, which led to profound changes, such as the 1917 Constitution. Over the 20th century, Mexico experienced significant economic growth; as well as issues of repression and electoral fraud. The late 20th century saw a shift towards neoliberal policies, exemplified by the signing of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) in 1994, amidst unrest in Chiapas.
Mexico is a newly industrialized and developing country,[17] with the world's 12th-largest economy by both nominal GDP and PPP. Mexico ranks first in the Americas and seventh in the world by the number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites.[18] It is also one of the world's 17 megadiverse countries, ranking fifth in natural biodiversity.[19] It is a major tourist destination: as of 2022, it is the sixth most-visited country in the world, with 42.2 million international arrivals.[20] Mexico's large economy and population, global cultural influence, and steady democratization make it a regional and middle power,[21][22][23] increasingly identifying as an emerging power.[24][25][26][27] However, as with much of Latin America, Mexico continues to struggle with poverty, systemic corruption, and extensive crime.[28] Since 2006, an ongoing conflict between drug trafficking syndicates has led to over 127,000 deaths.[29][30][31] Mexico is a member of United Nations, the G20, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the World Trade Organization (WTO), the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum, the Organization of American States, Community of Latin American and Caribbean States, and the Organization of Ibero-American States.
- ^ a b "Censo Población y Vivienda 2020". inegi.org.mx. INEGI. Archived from the original on 14 February 2022. Retrieved 26 January 2021.
- ^ "Political Constitution of the United Mexican States, title 2, article 40" (PDF). MX Q: SCJN. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 14 August 2010.
- ^ "Surface water and surface water change". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Archived from the original on 24 March 2021. Retrieved 11 October 2020.
- ^ "Total population by sex: Mexico". United Nations Population Division. Retrieved 1 January 2025.
- ^ "Census of Population and Housing 2020". INEGI. Retrieved 1 January 2025.
- ^ a b c d "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2024 Edition. (Mexico)". www.imf.org. International Monetary Fund. 22 October 2024. Retrieved 22 October 2024.
- ^ "El Inegi da a conocer los resultados de la Encuesta Nacional de Ingresos y Gastos de los Hogares (ENIGH) 2022" (PDF). 26 July 2023. p. 15. Retrieved 20 September 2024.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2023/24" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 March 2024. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- ^ INALI (13 March 2003). "General Law of Linguistic Rights of the Indigenous Peoples" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 August 2016. Retrieved 7 November 2010.
- ^ "Catálogo de las lenguas indígenas nacionales: Variantes lingüísticas de México con sus autodenominaciones y referencias geoestadísticas". Inali.gob.mx. Archived from the original on 8 July 2014. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ México in Diccionario panhispánico de dudas by Royal Spanish Academy and Association of Academies of the Spanish Language, Madrid: Santillana. 2005. ISBN 978-8-429-40623-8.
- ^ "Mexico". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 26 January 2021.
- ^ Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary, 3rd ed., Springfield, Massachusetts, United States, Merriam-Webster; p. 733
- ^ Brading, D.A., The First America: The Spanish Monarchy, Creole Patriots, and the Liberal State. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1991. ISBN 052139130X
- ^ Greenberg, Amy S. (2013). A wicked war : Polk, Clay, Lincoln, and the 1846 U.S. invasion of Mexico. New York. ISBN 978-0-307-47599-2. OCLC 818318029. Archived from the original on 21 February 2024. Retrieved 5 March 2022.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Garner, Paul. Porfirio Díaz. Routledge 2001.
- ^ Paweł Bożyk (2006). "Newly Industrialized Countries". Globalization and the Transformation of Foreign Economic Policy. Ashgate Publishing. p. 164. ISBN 978-0-7546-4638-9. Archived from the original on 4 November 2023. Retrieved 23 July 2018.
- ^ [1] Archived 4 February 2024 at the Wayback Machine UNESCO World Heritage sites, accessed 9 May 2022
- ^ "What is a mega-diverse country?". Mexican biodiversity. Archived from the original on 7 September 2019. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ^ "México ocupa el sexto lugar en turismo a nivel mundial". www.expansion.mx. CNN Expansión. 28 August 2018. Archived from the original on 23 December 2019. Retrieved 8 January 2019.
- ^ James Scott; Matthias vom Hau; David Hulme. "Beyond the BICs: Strategies of influence". The University of Manchester. Archived from the original on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 11 April 2012.
- ^ Nolte, Detlef (October 2010). "How to compare regional powers: analytical concepts and research topics". Review of International Studies. 36 (4): 881–901. doi:10.1017/S026021051000135X. ISSN 0260-2105. JSTOR 40961959. S2CID 13809794. ProQuest 873500719. Archived from the original on 2 March 2021. Retrieved 17 November 2020.
- ^ "Oxford Analytica". Archived from the original on 24 April 2007. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- ^ "G8: Despite Differences, Mexico Comfortable as Emerging Power". ipsnews.net. 5 June 2007. Archived from the original on 16 August 2008. Retrieved 30 May 2010.
- ^ Mauro F. Guillén (2003). "Multinationals, Ideology, and Organized Labor". The Limits of Convergence. Princeton University Press. p. 126 (table 5.1). ISBN 978-0-691-11633-4. Archived from the original on 21 February 2024. Retrieved 23 July 2018.
- ^ David Waugh (2000). "Manufacturing industries (chapter 19), World development (chapter 22)". Geography, An Integrated Approach (3rd ed.). Nelson Thornes. pp. 563, 576–579, 633, and 640. ISBN 978-0-17-444706-1. Archived from the original on 4 February 2024. Retrieved 23 July 2018.
- ^ N. Gregory Mankiw (2007). Principles of Economics (4th ed.). Mason, Ohio: Thomson/South-Western. ISBN 978-0-324-22472-6. Archived from the original on 4 February 2024. Retrieved 23 July 2018.
- ^ "Global Peace Index 2019: Measuring Peace in a Complex World" (PDF). Vision of Humanity. Sydney: Institute for Economics & Peace. June 2019. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 August 2019. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- ^ "UCDP - Uppsala Conflict Data Program 2023". ucdp.uu.se. 31 May 2024. Archived from the original on 31 May 2024. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ^ "Mexico". ucdp.uu.se. UCDP – Uppsala Conflict Data Program. Archived from the original on 27 March 2022. Retrieved 16 June 2021.
- ^ "Opinión: Una guerra inventada y 350,000 muertos en México". Washington Post. 14 June 2021. Archived from the original on 9 May 2022. Retrieved 15 December 2023.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).