
Back Mid-Atlantiese Rug Afrikaans حيد وسط المحيط الأطلسي Arabic Dorsal mesoatlántica AST Orta Atlantika silsiləsi Azerbaijani Сярэдзінна-Атлантычны хрыбет Byelorussian Средноатлантически хребет Bulgarian মধ্য-আটলান্টিক শৈলশিরা Bengali/Bangla Dorsal mesoatlàntica Catalan Йуккъера-Атлантикин дукъ CE Středoatlantský hřbet Czech
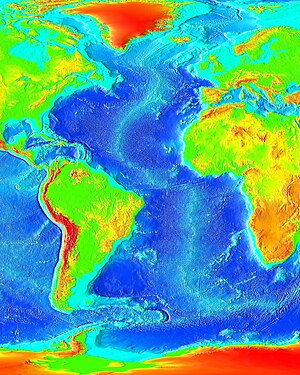
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge (a divergent or constructive plate boundary) located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, and part of the longest mountain range in the world. In the North Atlantic, the ridge separates the North American from the Eurasian plate and the African plate, north and south of the Azores triple junction. In the South Atlantic, it separates the African and South American plates. The ridge extends from a junction with the Gakkel Ridge (Mid-Arctic Ridge) northeast of Greenland southward to the Bouvet triple junction in the South Atlantic. Although the Mid-Atlantic Ridge is mostly an underwater feature, portions of it have enough elevation to extend above sea level, for example in Iceland. The ridge has an average spreading rate of about 2.5 centimetres (1 in) per year.[1]
- ^ "Understanding plate motions". United States Geological Survey. 5 May 1999. Retrieved 13 March 2011.