Back Fosforsuur Afrikaans حمض الفسفوريك Arabic Ácidu fosfórico AST فوسفوریک اسید AZB Фосфорна киселина Bulgarian ফসফরিক অ্যাসিড Bengali/Bangla Fosforna kiselina BS Àcid fosfòric Catalan Kyselina fosforečná Czech Asid ffosfforig Welsh
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Phosphoric acid
| |||
| Other names
Orthophosphoric acid, hydrogen phosphate
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.758 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| E number | E338 (antioxidants, ...) | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1805 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
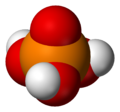
| H3PO4 | |||
| Molar mass | 97.994 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless solid | ||
| Odor | Odorless | ||
| Density | 1.6845 g/cm3 (25 °C, 85%),[1] 1.834 g/cm3 (solid)[2] | ||
| Melting point | 42.35 °C (108.23 °F; 315.50 K) anhydrous[12] 29.32 °C (84.78 °F; 302.47 K) hemihydrate[13] | ||
| Boiling point | |||
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol | ||
| log P | −2.15[7] | ||
| Vapor pressure | 0.03 mmHg (20 °C)[8] | ||
| Conjugate base | Dihydrogen phosphate | ||
| −43.8·10−6 cm3/mol[10] | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
| ||
| Viscosity | 2.4–9.4 cP (85% aq. soln.) 147 cP (100%) | ||
| Structure | |||
| Monoclinic | |||
| Tetrahedral | |||
| Thermochemistry[14] | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
145.0 J/(mol⋅K) | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
150.8 J/(mol⋅K) | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−1271.7 kJ/mol | ||
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵)
|
−1123.6 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 [15] [15]
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H290, H314[15] | |||
| P280, P305+P351+P338, P310[15] | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | Non-flammable | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
1530 mg/kg (rat, oral)[16] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3[8] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 ST 3 mg/m3[8] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
1000 mg/m3[8] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 1008 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related phosphorus oxoacids
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Phosphoric acid (orthophosphoric acid, monophosphoric acid or phosphoric(V) acid) is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula H3PO4. It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, which is a colourless, odourless, and non-volatile syrupy liquid. It is a major industrial chemical, being a component of many fertilizers.
The compound is an acid. Removal of all three H+ ions gives the phosphate ion PO3−4. Removal of one or two protons gives dihydrogen phosphate ion H2PO−4, and the hydrogen phosphate ion HPO2−4, respectively. Phosphoric acid forms esters, called organophosphates.[17]
The name "orthophosphoric acid" can be used to distinguish this specific acid from other "phosphoric acids", such as pyrophosphoric acid. Nevertheless, the term "phosphoric acid" often means this specific compound; and that is the current IUPAC nomenclature.
- ^ Christensen, J. H.; Reed, R. B. (1955). "Design and Analysis Data—Density of Aqueous Solutions of Phosphoric Acid Measurements at 25 °C". Ind. Eng. Chem. 47 (6): 1277–1280. doi:10.1021/ie50546a061.
- ^ "CAMEO Chemicals Datasheet – Phosphoric Acid". Archived from the original on 15 August 2019. Retrieved 15 August 2019.
- ^ "Phosphoric acid". www.chemspider.com. Archived from the original on 12 March 2020. Retrieved 3 March 2020.
- ^ Brown, Earl H.; Whitt, Carlton D. (1952). "Vapor Pressure of Phosphoric Acids". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry. 44 (3): 615–618. doi:10.1021/ie50507a050.
- ^ Seidell, Atherton; Linke, William F. (1952). Solubilities of Inorganic and Organic Compounds. Van Nostrand. Archived from the original on 11 March 2020. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- ^ Haynes, p. 4.80
- ^ "phosphoric acid_msds". Archived from the original on 4 July 2017. Retrieved 2 May 2018.
- ^ a b c d NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0506". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Haynes, p. 5.92
- ^ Haynes, p. 4.134
- ^ Edwards, O. W.; Dunn, R. L.; Hatfield, J. D. (1964). "Refractive Index of Phosphoric Acid Solutions at 25 C.". J. Chem. Eng. Data. 9 (4): 508–509. doi:10.1021/je60023a010.
- ^ Greenwood, N. N.; Thompson, A. (1959). "701. The mechanism of electrical conduction in fused phosphoric and trideuterophosphoric acids". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 3485. doi:10.1039/JR9590003485.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Rosswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Haynes, p. 5.13
- ^ a b c Sigma-Aldrich Co., Phosphoric acid.
- ^ "Phosphoric acid". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Westheimer, F.H. (6 June 1987). "Why nature chose phosphates". Science. 235 (4793): 1173–1178 (see pp. 1175–1176). Bibcode:1987Sci...235.1173W. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.462.3441. doi:10.1126/science.2434996. PMID 2434996.