Back حيود المسحوق Arabic Debye-Scherrer-Verfahren German Difracción de polvo Spanish پراش پودر Persian Diffraction sur poudre French Díraonadh púdar Irish Rendgenska strukturna analiza Croatian Poederdiffractie Dutch Difração de pó Portuguese Порошковая рентгеновская дифракция Russian

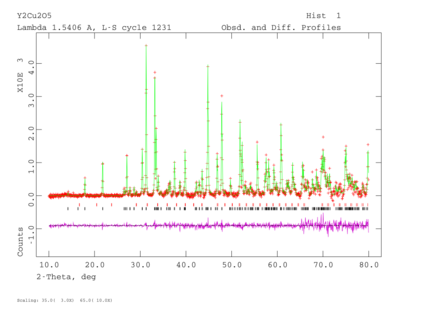
X-ray powder diffraction of Y2Cu2O5 and Rietveld refinement with two phases, showing 1% of yttrium oxide impurity (red tickers).
Powder diffraction is a scientific technique using X-ray, neutron, or electron diffraction on powder or microcrystalline samples for structural characterization of materials.[2] An instrument dedicated to performing such powder measurements is called a powder diffractometer.
Powder diffraction stands in contrast to single crystal diffraction techniques, which work best with a single, well-ordered crystal.
- ^ P. Fraundorf & Shuhan Lin (2004). "Spiral powder overlays". Microscopy and Microanalysis. 10 (S02): 1356–1357. Bibcode:2004MiMic..10S1356F. doi:10.1017/S1431927604884034. S2CID 17009500.
- ^ B.D. Cullity Elements of X-ray Diffraction Addison Wesley Mass. 1978 ISBN 0-201-01174-3