
Back حفرة جناحية حنكية Arabic Fossa pterygopalatina German Fosa pterigopalatina Spanish Pterigoide-ahosabaietako hobi Basque گودی بالیکامی Persian Fosse ptérygo-palatine French Fosa pterigomaxilar Galician Fossa pterigopalatina Italian Foso pterigopalatal LFN Fossa pterygopalatina NB
| Pterygopalatine fossa | |
|---|---|
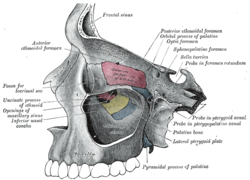 Left maxillary sinus opened from the exterior. | |
 Human skull with entrance to pterygopalatine fossa marked in red | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fossa pterygopalatina |
| MeSH | D056739 |
| TA98 | A02.1.00.025 |
| TA2 | 429 |
| FMA | 75309 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
In human anatomy, the pterygopalatine fossa (sphenopalatine fossa) is a fossa in the skull. A human skull contains two pterygopalatine fossae—one on the left side, and another on the right side. Each fossa is a cone-shaped paired depression deep to the infratemporal fossa and posterior to the maxilla on each side of the skull, located between the pterygoid process and the maxillary tuberosity close to the apex of the orbit.[1] It is the indented area medial to the pterygomaxillary fissure leading into the sphenopalatine foramen. It communicates with the nasal and oral cavities, infratemporal fossa, orbit, pharynx, and middle cranial fossa through eight foramina.[2]
- ^ Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 69
- ^ Osborn, Anne (March 1979). "Radiology of the Pterygoid Plates and Pterygopalatine Fossa" (PDF). American Journal of Roentgenology. 132 (3): 389–394. doi:10.2214/ajr.132.3.389. PMID 106641.