
Back حالة تسابق Arabic Yarış durumu Azerbaijani یاریشما دورومو AZB Situació de competició Catalan Souběh Czech Wettlaufsituation German Konkura kondiĉo Esperanto Condición de carrera Spanish وضعیت رقابتی Persian Situation de compétition French
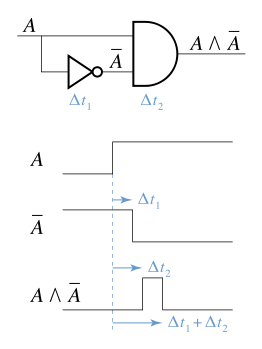
A race condition or race hazard occurs in electronics, software, or other system when the system's behavior depends on the timing or order of uncontrollable events, leading to unpredictable outcomes. In software, race conditions occur when multiple threads or processes attempt to access or change a variable, file, or other resource at the same time without proper synchronization.[1] In logic circuits, race conditions arise when signals traveling along different paths reach a component at different times, resulting in unexpected outputs.
- ^ von Praun, Christoph (2011), Padua, David (ed.), "Race Conditions", Encyclopedia of Parallel Computing, Boston, MA: Springer US, pp. 1691–1697, doi:10.1007/978-0-387-09766-4_36, ISBN 978-0-387-09766-4, retrieved 2025-01-23