
Back النموذج اللوني المعياري أحمر أخضر أزرق Arabic SRGB BAN SRGB Byelorussian Espai de color sRGB Catalan SRGB Czech SRGB-Farbraum German Espacio de color sRGB Spanish SRGB Estonian SRGB Finnish SRGB French
| IEC 61966-2-1 Default RGB Colour Space - sRGB | |
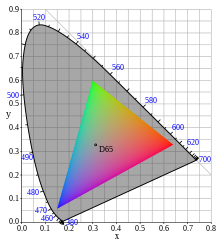 sRGB colors situated at calculated position in CIE 1931 chromaticity diagram. Y=1/3 which is the brightest luminance where the whole triangle exists. | |
| Abbreviation | sRGB |
|---|---|
| Status | Published |
| Year started | 1996 |
| First published | October 18, 1999[1] |
| Organization | IEC[1] |
| Committee | TC/SC: TC 100/TA 2[1] |
| Base standards | IEC 61966 Colour Measurement and Management in Multimedia Systems and Equipment |
| Domain | Color space, color model |
| Website | webstore |
sRGB is an RGB (red, green, blue) colorspace, for use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web. It was initially proposed by HP and Microsoft in 1996[2] and became an official standard of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as IEC 61966-2-1:1999.[1] It is the current standard colorspace for the web, and it is usually the assumed colorspace for images that do not have an embedded color profile.
The sRGB standard uses the same color primaries and white point as the ITU-R BT.709 standard for HDTV,[3] but a different transfer function (or gamma) compatible with the era's CRT displays,[4] and assumes a viewing environment closer to typical home and office viewing conditions. Matching the behavior of PC video cards and CRT displays greatly aided sRGB's popularity.
- ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
IEC1999was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
IEC1996draftwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
poyn2003was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
ImEn2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page).