
Back العلامات والأعراض Arabic নিদর্শন ও লক্ষণ-উপসর্গ Bengali/Bangla Znakovi i simptomi BS Signes i símptomes Catalan علائم و نشانههای بیماری Persian Symptômes et signes médicaux French Ախտանիշ Armenian 症状と徴候 Japanese 징후 및 증상 Korean രോഗലക്ഷണങ്ങളും അടയാളങ്ങളും Malayalam
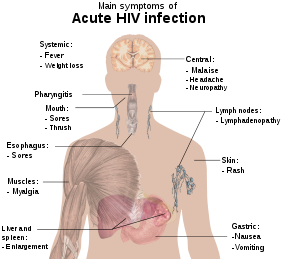
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition.
Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences.[1]
A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pains in the body,[2][3] which occur as the body's immune system fights off an infection.[4][5][6]
- ^ Sadock BJ, Sadock VA (2008). Kaplan & Sadock's Concise Textbook of Clinical Psychiatry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-8746-8. Archived from the original on 6 January 2023. Retrieved 6 January 2023.
- ^ "Beyond Intuition: Quantifying and Understanding the Signs and Symptoms of Fever". clinicaltrials.gov. 5 October 2017. Archived from the original on 13 February 2022. Retrieved 9 January 2021.
- ^ "Symptoms and self-help guides by body part". NHS inform. Archived from the original on 13 February 2022. Retrieved 9 January 2021.
- ^ "How Infection Works, How Pathogens Make Us Sick — The National Academies". needtoknow.nas.edu. Retrieved 29 November 2024.
- ^ "Infectious Diseases". Cleveland Clinic. 6 June 2022. Retrieved 29 November 2024.
- ^ "Immune System". Cleveland Clinic. 20 October 2023. Retrieved 29 November 2024.