
Back Republica Socialista de Bosnia y Herzegovina AN جمهورية البوسنة والهرسك الاشتراكية Arabic Bosniya və Herseqovina Sosialist Respublikası Azerbaijani Босния һәм Герцеговина Социалистик Республикаһы Bashkir Сацыялістычная Рэспубліка Боснія і Герцагавіна Byelorussian Сацыялістычная Рэспубліка Босьнія і Герцагавіна BE-X-OLD Социалистическа република Босна и Херцеговина Bulgarian Socijalistička Republika Bosna i Hercegovina BS República Socialista de Bòsnia i Hercegovina Catalan Socialistická republika Bosna a Hercegovina Czech
Democratic Bosnia and Herzegovina (1943–1945) Demokratska Bosna i Hercegovina (Serbo-Croatian) Federal State of Bosnia and Herzegovina (1945–1946) People's Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (1946–1963) Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (1963–1992) Socijalistička Republika Bosna i Hercegovina (Serbo-Croatian) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1943–1992 | |||||||||||||||||
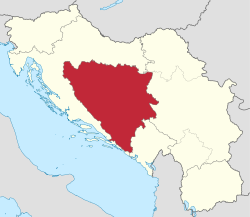 Location of Bosnia and Herzegovina in Yugoslavia. | |||||||||||||||||
| Status | Constituent republic of Yugoslavia | ||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Sarajevo | ||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Serbo-Croatian | ||||||||||||||||
| Government | 1945–1948: Marxist–Leninist one-party socialist republic 1948–1990: Titoist one-party socialist republic 1990–1992: Parliamentary constitutional republic | ||||||||||||||||
| Chairman of the Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina | |||||||||||||||||
• 1945–1946 (first) | Vojislav Kecmanović | ||||||||||||||||
• 1990–1992 (last) | Alija Izetbegović | ||||||||||||||||
| Chairman of the Council of Ministers of Bosnia and Herzegovina | |||||||||||||||||
• 1945–1948 (first) | Rodoljub Čolaković | ||||||||||||||||
• 1990–1992 (last) | Jure Pelivan | ||||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Parliament of Bosnia and Herzegovina | ||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Cold War | ||||||||||||||||
• ZAVNOBiH | 25 November 1943 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18 November 1991 | |||||||||||||||||
• Republika Srpska formed | 9 January 1992 | ||||||||||||||||
| 1 March 1992 | |||||||||||||||||
• Outbreak of Bosnian War | 5 April 1992 | ||||||||||||||||
• Independence | 6 April 1992 | ||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||
• Total | 51,129 km2 (19,741 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | BA | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| History of Bosnia and Herzegovina |
|---|
 |
|
|
The Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (Serbo-Croatian: Socijalistička Republika Bosna i Hercegovina / Социјалистичка Pепублика Босна и Херцеговина), commonly referred to as Socialist Bosnia or simply Bosnia, was one of the six constituent federal states forming the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. It was a predecessor of the modern-day Bosnia and Herzegovina, existing between 1945 and 1992, under a number of different formal names, including Democratic Bosnia and Herzegovina (1943–1946) and People's Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (1946–1963).
Within Yugoslavia, Bosnia and Herzegovina was a unique federal state with no dominant ethnic group, as was the case in other constituent states, all of which were also nation states of Yugoslavia's South Slavic ethnic groups. It was administered under strict terms of sanctioned consociationalism, known locally as "ethnic key" or "national key" (Serbo-Croatian: etnički/nacionalni ključ), based on the balance of political representation of 3 largest ethnic groups (Bosnian Muslims,[a] Croats and Serbs).
Sarajevo served as the capital city throughout its existence and remained the capital following independence. The Socialist Republic was dissolved in 1990 when it abandoned its socialist institutions and adopted liberal ones, as the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina which declared independence from Yugoslavia in 1992. The Government of Bosnia and Herzegovina was, up to 20 December 1990, in sole control of the League of Communists of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Bosnian branch of League of Communists of Yugoslavia.
The borders of SR Bosnia and Herzegovina were almost identical to the one Condominium of Bosnia and Herzegovina had during the period of Austro-Hungarian rule that lasted until 1918. That year Bosnia became part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes and divided into several banovinas (regional administrative units), namely parts of Vrbas, Drina, Zeta and Croatia banovinas. With the establishment of a People's Republic, its modern borders were delineated.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).

