
Back ذروة شمسية Arabic Màxim solar Catalan Máximo solar Spanish Maximum solaire French सौर अधिकतम Hindi Massimo solare Italian 太陽極大期 Japanese 태양 극대기 Korean Zonnemaximum Dutch Solmaksimum NN

Solar maximum is the regular period of greatest solar activity during the Sun's 11-year solar cycle. During solar maximum, large numbers of sunspots appear, and the solar irradiance output grows by about 0.07%.[2] On average, the solar cycle takes about 11 years to go from one solar maximum to the next, with duration observed varying from 9 to 14 years.
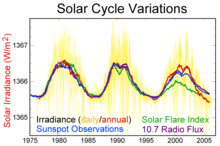
Large solar storms often occur during solar maximum. For example, the Carrington Event, which took place a few months before the solar maximum of solar cycle 10, was the most intense geomagnetic storm in recorded history and widely considered to have been caused by an equally large solar storm.[3]
- ^ NASA
- ^ C. D. Camp & K. K. Tung (2007). "Surface warming by the solar cycle as revealed by the composite mean difference projection" (PDF). Geophysical Research Letters. 34 (14): L14703. Bibcode:2007GeoRL..3414703C. doi:10.1029/2007GL030207. Retrieved 20 January 2012.
- ^ "Monster radiation burst from Sun". BBC News. 14 May 2013. Retrieved 2015-01-06.